Living with IDDM can be challenging for children and their
families. However, with the right strategies, coping becomes more manageable.
Support Groups
Joining support groups can provide a sense of community and
understanding, allowing families to share their experiences and learn from one
another.
Psychological Support
Counseling and therapy can help children and their families
navigate the emotional and psychological challenges that come with IDDM.
Regular Medical Check-ups

Regular medical check-ups are a crucial aspect of managing Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus (IDDM) in children. These check-ups help monitor the child's health, assess the effectiveness of the treatment plan, and make any necessary adjustments. During these appointments, healthcare professionals will check Blood Sugar Levels. Regular blood sugar level assessments provide valuable information about the child's glucose control. By analyzing the data, healthcare providers can identify patterns and make informed decisions about insulin dosages.
Assess HbA1c Levels: Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) is a marker that indicates the average blood sugar levels over the past few months. Monitoring HbA1c levels helps assess long-term glucose control and provides insight into the child's overall health.
Examine for Complications
Healthcare professionals will also conduct physical examinations to check for any signs of diabetes-related complications, such as retinopathy, neuropathy, and kidney issues.
Review Diet and Exercise
During check-ups, healthcare providers may review the child's dietary habits and physical activity levels. They can offer guidance and adjustments to help improve glucose management.
Supporting Children in Emergency Situations
In emergencies, such as severe hypoglycemia or diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), it is crucial for parents, caregivers, and teachers to know how to respond promptly.
Recognizing Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia occurs when blood sugar levels drop too low. Symptoms may include shakiness, confusion, sweating, and dizziness. Administering a quick-acting source of sugar, such as glucose tablets or juice, can help raise blood sugar levels rapidly.
Managing Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)
DKA is a life-threatening condition that occurs when blood sugar levels are excessively high, and the body starts breaking down fat for energy, producing ketones. Symptoms include dehydration, fruity breath odor, confusion, and rapid breathing. DKA requires immediate medical attention and treatment with insulin and fluids.
Addressing Emotional and Psychological Well-being
Living with IDDM can have a significant emotional impact on children and their families. Addressing the emotional and psychological well-being of the child is an integral part of their overall health.
Open Communication
Encouraging open communication within the family and providing a safe space for the child to express their feelings can help them cope with the challenges of living with IDDM.
Identifying Signs of Emotional Distress
Parents and caregivers should be vigilant for signs of emotional distress in children, such as changes in behavior, mood swings, or withdrawal. Seeking professional help, such as counseling or therapy, can provide additional support.
Promoting a Healthy Lifestyle
A healthy lifestyle is fundamental in managing IDDM effectively and promoting overall well-being.
Balanced Diet
A balanced diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains, supports glucose control and overall health. Limiting sugary and processed foods can help prevent blood sugar spikes.
Regular Physical Activity
Encouraging children to engage in regular physical activity benefits their physical and mental health. Physical activity can also improve insulin sensitivity and help manage blood sugar levels.

Adequate Sleep
Getting enough restful sleep is essential for children with IDDM. Proper sleep supports glucose regulation and overall health.
Nurturing Independence and Self-Management
As children grow older, encouraging them to take an active role in their diabetes management can foster independence and self-confidence.
Learning Self-Monitoring
Teaching children how to monitor their blood sugar levels and administer insulin empowers them to manage their condition more independently.

Problem-Solving Skills
Encouraging problem-solving skills equips children to handle diabetes-related challenges and adapt to different situations confidently.
Building a Support Network
Supportive family members, friends, and healthcare professionals can play a vital role in empowering children to take charge of their diabetes management.
Embracing Hope for the Future
While living with IDDM poses challenges, it is essential to maintain hope for a bright and fulfilling future.
Research Advancements
Ongoing research and medical advancements offer hope for improved treatments, better management tools, and eventually, a cure for IDDM.
Personal Growth
Children with IDDM can develop resilience, empathy, and determination as they navigate life with the condition. These qualities contribute to their personal growth and success.

Positive Role Models
Providing children with positive role models, such as successful individuals living with diabetes, can inspire them to pursue their dreams and overcome obstacles.
Prevention and Early Intervention
While IDDM cannot be entirely prevented, there are measures
that can reduce the risk of its onset or delay its progression.
Genetic Testing
If there is a family history of IDDM, genetic testing can
help identify individuals who might be at a higher risk. Early identification
allows for proactive measures and regular monitoring.
Vaccinations
Some studies suggest a possible link between viral infections and the development of IDDM. Staying up-to-date with vaccinations may help reduce the risk of certain infections.
Breastfeeding
Breastfeeding has been associated with a reduced risk of
IDDM in children with a genetic predisposition. Encouraging breastfeeding for
the recommended duration can offer potential benefits.
The Role of Technology in IDDM Management
Advancements in technology have revolutionized IDDM
management, making it more efficient and convenient.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)
CGM devices continuously measure glucose levels throughout
the day and night. They provide real-time data, allowing for better management
and immediate adjustments to insulin doses.
Insulin Pumps
Insulin pumps are small devices that deliver insulin
continuously, closely mimicking the body's natural insulin release. They offer
more flexibility in insulin dosing and are particularly useful for children
with busy lifestyles.
Artificial Pancreas Systems
Artificial pancreas systems combine CGM and insulin pump
technology to automate insulin delivery. These systems can significantly
improve blood sugar control and reduce the burden of constant monitoring.

Addressing School and Social Life Challenges

Children with IDDM often face unique challenges in school
and social settings. Open communication and awareness are essential for a
supportive environment.
School Accommodations
Working with teachers and school staff to create a diabetes
management plan ensures that the child's needs are met during school hours.
This may involve accommodating insulin administration, snack breaks, and access
to necessary supplies.
Peer Education
Educating classmates about IDDM can foster understanding and empathy. Encouraging children with IDDM to share their experiences can reduce stigma and create a supportive social environment.

Travel and Extracurricular Activities
With proper planning and communication, children with IDDM
can participate in various extracurricular activities and travel. Caregivers
must ensure they have enough supplies and know how to manage diabetes in
different situations.
Promising Research and Treatment Developments
Medical research continues to explore innovative treatments
and potential cures for IDDM. Some promising areas of study include:
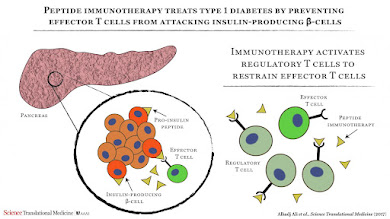
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy aims to modify the immune system's response to prevent it from attacking the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
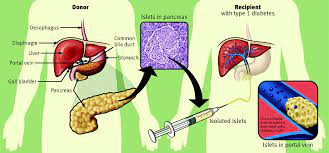
Islet Cell Transplantation
Islet cell transplantation involves transplanting healthy insulin-producing cells into the pancreas, offering a potential cure for IDDM.
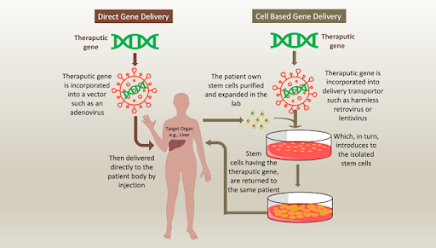
Gene Therapy
Gene therapy seeks to correct the genetic defects
responsible for IDDM, potentially preventing its development altogether.

The Importance of Emotional Support
Living with IDDM can be emotionally challenging for children
and their families. Emotional support is just as crucial as medical management.
Family Dynamics
Open communication within the family helps everyone
understand and cope with the challenges of managing IDDM. Offering emotional
support to each other strengthens family bonds.
Peer Support Groups
Peer support groups allow children with IDDM to connect with
others facing similar experiences, fostering a sense of belonging and
normalizing their condition.
Mental Health Care
Children with IDDM may experience stress and anxiety related
to their condition. Access to mental health care can help them develop coping
strategies and build resilience.
Empowering Children for a Bright Future

While IDDM presents challenges, it doesn't define a child's
future. Empowerment and self-management are essential for a positive outlook.
Education and Knowledge
As children grow older, involving them in their diabetes
management builds responsibility and self-confidence. Educating them about
their condition equips them to make informed decisions.
Setting Goals
Encouraging children to set achievable goals fosters a sense
of accomplishment and motivates them to take charge of their health.
Fostering Independence
Gradually allowing children to take on more responsibilities
related to their IDDM instills a sense of independence and self-reliance.
Advocacy and Awareness
Advocacy for diabetes research, access to healthcare, and
public awareness is essential in creating a supportive environment for children
with IDDM. By joining advocacy efforts and spreading awareness, we can foster
understanding and reduce the stigma surrounding the condition.
Continuing Research and Innovation
The landscape of diabetes management is constantly evolving,
with new treatments and technologies emerging. Supporting and participating in
diabetes research contributes to the development of more effective treatments
and, eventually, a cure.
Community and Support
Being part of a supportive community can make a significant
difference in the lives of children with IDDM and their families. Connecting
with others who understand the challenges and triumphs of living with IDDM can
provide invaluable emotional support.
Additional Resources
As part of my commitment to being a reliable and
comprehensive resource, I have compiled a list of reputable organizations and
websites that offer further information and support related to Insulin
Dependent Diabetes Mellitus in children:
- Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation (JDRF): An organization
dedicated to funding research and advocating for the prevention, treatment, and
cure of Type 1 diabetes.
- American Diabetes Association (ADA): A leading organization
providing information, resources, and support for individuals and families
affected by diabetes.
- Beyond Type 1: An organization that offers a supportive
community for those living with Type 1 diabetes, providing resources, stories,
and advocacy opportunities.
- Children with Diabetes (CWD): An online community providing
support and education for families and children living with diabetes.
Embracing Hope and Building Resilience
Living with IDDM may present challenges, but it also fosters
strength, resilience, and a determination to overcome obstacles. By arming
ourselves with knowledge, embracing hope, and supporting each other, we can
ensure that children with IDDM lead fulfilling lives and achieve their dreams.
At https://healthponder.blogspot.com/,
I am committed to being a reliable source of information, continuously updating
my content to reflect the latest advancements in diabetes management and
research. Remember, with the right support, education, and medical
care, children with IDDM can lead happy, healthy lives and confidently face the
future.
https://freemoviesforfun.blogspot.com/

















Comments
Post a Comment
If you have any query, doubt or seek any advice or help, I am always available.